-
Term: Focus Mode
Description: A camera's focus mode is the main setting of either autofocus or manual focus. This mode is often changed by a physical switch on the camera, labeled "AF/MF" or on a dial and/or button. Within autofocus, there are often two or three different focus modes as well depending on your camera make and model:- Single Focus - the camera only tries to focus on the subject once and then stops
- Continuous Focus - the camera will continually adjust focus to track a moving subject
- Auto mode - the camera determines for you whether to focus in Single or Continuous.
Focus Mode
Mastering Focus Modes: A Guide for Photographers
As a photographer, achieving sharp and accurate focus is crucial to producing high-quality images. With the wide range of focus modes available on modern cameras, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for each situation. In this guide, we’ll explain the different types of focus modes available, and provide tips on how to use them effectively to take your photography to the next level.
Before diving into the various focus modes available, it’s important to understand why focus modes are so critical in photography. Having control over the focus of your images allows you to create a sense of depth and highlight important details, making your photos more visually engaging. With a solid understanding of focus modes, you can have confidence that your images will be tack-sharp and highly detailed.
Manual Focus Mode

Manual focus mode is the most basic type of focus mode available on most cameras. In this mode, the photographer must physically adjust the focus ring on the lens to achieve the desired focus. While it may seem archaic in a world of sophisticated autofocus systems, manual focus can be highly effective in certain situations. For example, if you’re shooting a still life and want to carefully control which elements are in focus, manual focus is ideal. Additionally, manual focus can be useful in low-light situations where autofocus struggles to lock onto a subject.
Autofocus Mode

Autofocus mode is the most commonly used focus mode in photography. In this mode, the camera’s autofocus system analyzes the scene and attempts to focus on the most important element. There are several different autofocus modes available, including single-shot autofocus, continuous autofocus, and automatic autofocus. Single-shot autofocus is best for still subjects, while continuous autofocus is ideal for moving subjects. Automatic autofocus is a versatile mode that automatically switches between single-shot and continuous autofocus depending on the scene.
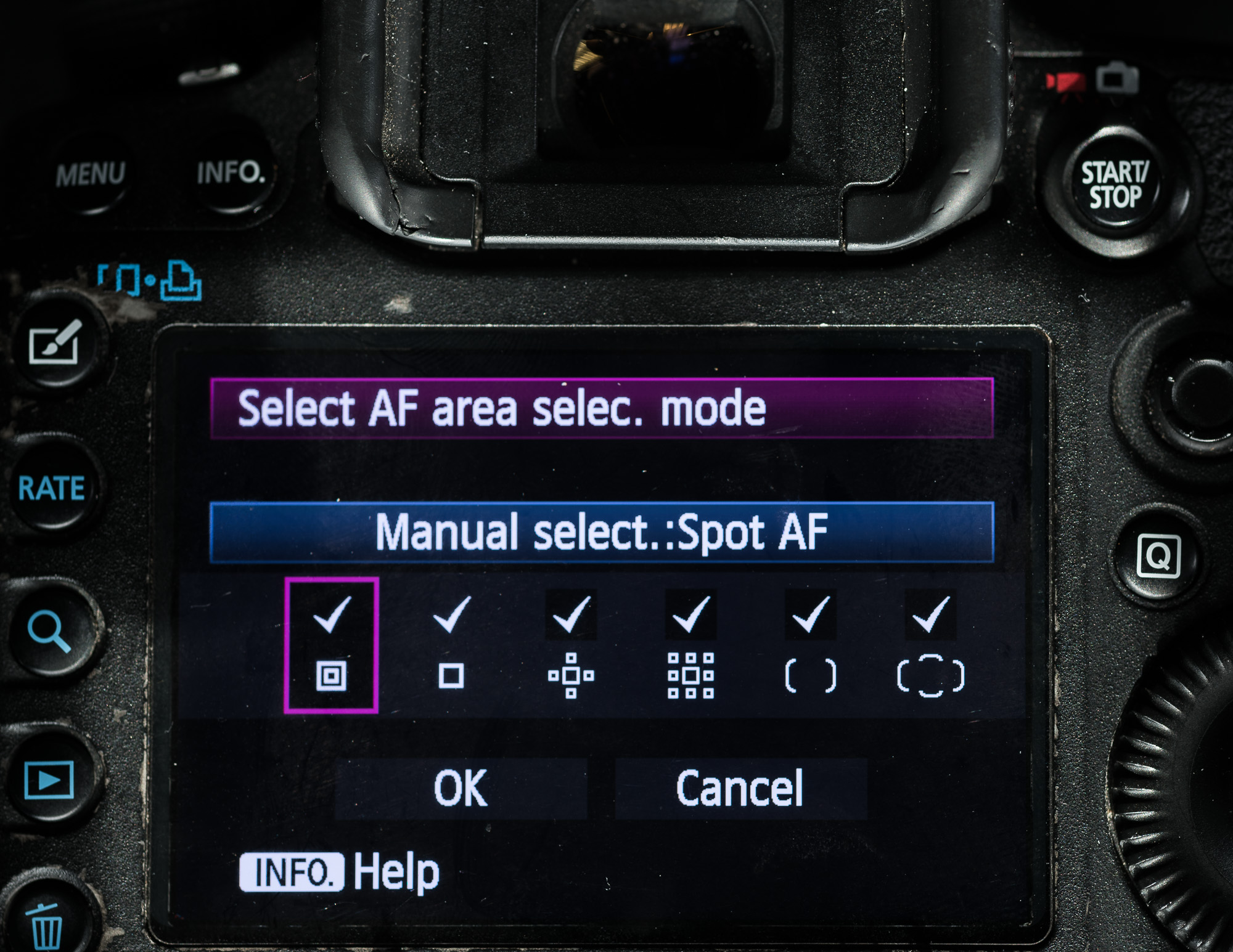
When using autofocus, it’s important to remember that the camera may not always focus on the subject you intended. It’s a good idea to experiment with the different autofocus modes to determine which mode is best for each situation.
Back-Button Focus

Back-button focus is a more advanced focus mode that separates autofocus from the shutter button. In this mode, the autofocus is activated using a button on the back of the camera, while the shutter button is used solely for taking the photo. This mode allows for greater control over the focus, as it prevents the camera from refocusing when the shutter button is pressed. Back-button focus can be particularly useful for sports and wildlife photography, where the subject is constantly moving.
Hybrid Focus Modes
Hybrid focus modes, such as Canon’s Dual Pixel AF and Nikon’s Hybrid AF, combine elements of both manual and autofocus modes. These modes allow the photographer to manually adjust the focus while also relying on autofocus assistance. The result is a more natural, intuitive focus experience that is particularly useful for video and live-view shooting.
Focus Recomposing vs. AF Point Selection

Focus recomposing involves focusing on the subject with the autofocus system, and then recomposing the shot by moving the camera to position the subject where you want it in the frame. AF point selection, on the other hand, allows the photographer to manually select the autofocus point on the camera, ensuring that the subject is in sharp focus in the exact spot they want it to be. While both methods can be effective in certain situations, AF point selection is generally considered to be more accurate and reliable, particularly when shooting with a wide aperture or in low light conditions.
Conclusion
By mastering the various focus modes available on your camera, you can take your photography to the next level. Manual focus mode provides complete control over focus, while autofocus mode is ideal for quickly capturing a moment. Back-button focus and hybrid focus modes provide additional options for photographers who need greater control over their focus. Experiment with the different focus modes to find what works best for your shooting style, and be sure to practice regularly to improve your technique. With these tips and a little bit of practice, you’ll be well on your way to capturing tack-sharp, high-quality images.
Related Reading for Focus Modes in Photography
See related subjects to Focus Mode:Autofocus Definition
Continuous Autofocus Definition
AI-Servo Autofocus Definition
Single/One-Shot Autofocus Definition




Get Connected!